The difference between RF isolators and RF circulators
In practical applications, RF isolators and RF circulators are often mentioned simultaneously.
What is the relationship between RF isolators and RF circulators? What's the difference?
This article will focus on discussing these issues.
Radio frequency isolator, also known as a unidirectional device, is a device that transmits electromagnetic waves in one direction. When the electromagnetic waves propagate in the forward direction, they can feed all the power to the load and cause significant attenuation of the reflected waves from the load.This unidirectional transmission characteristic can be used to isolate the impact of load changes on the signal source.
RF circulators are branch transmission systems with non reciprocal characteristics. The commonly used ferrite RF circulators are Y-shaped junction RF circulators, which are composed of three branch lines symmetrically distributed at an angle of 120 ° to each other.
1、 What is an RF isolator?
Radio frequency isolator, also known as a unidirectional device, is a device that transmits electromagnetic waves in one direction. When the electromagnetic waves propagate in the forward direction, they can feed all the power to the load and cause significant attenuation of the reflected waves from the load. This unidirectional transmission characteristic can be used to isolate the impact of load changes on the signal source. Taking the field moving isolator as an example, further explain the working principle of ferrite RF isolator.
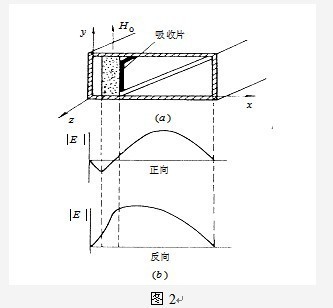
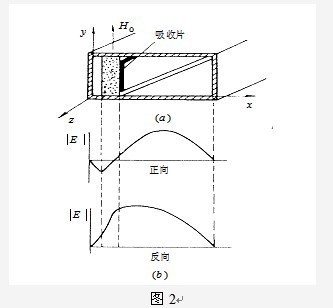
Field shift isolators are made based on the different field shift effects of ferrite on the wave modes transmitted in two directions. It adds attenuation plates on the side of the ferrite sheet, and due to the different deviations of the fields generated by the two directions of transmission, the electric field of the wave transmitted in the forward direction (- z direction) is biased towards the side without attenuation plates, while the electric field of the wave transmitted in the reverse direction (+z direction) is biased towards the side of attenuation plates, thus achieving the isolation function of small forward attenuation and large reverse attenuation, as shown in Figure 2.
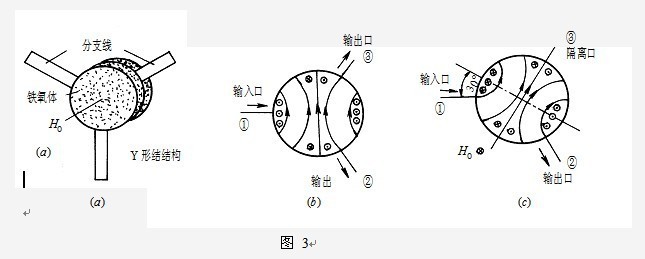
2、 What is an RF circulators?
RF circulators are branch transmission systems with non reciprocal characteristics. The commonly used ferrite RF circulators are Y-shaped RF circulators, as shown in Figure 3 (a), which are composed of three branch lines symmetrically distributed at an angle of 120 ° to each other. When the external magnetic field is zero, the ferrite is not magnetized, so the magnetism in all directions is the same. When the signal is input from branch line "①", a magnetic field as shown in Figure 3 (b) will be excited at the ferrite junction. Due to the same conditions for branches "②, ③", the signal is output in equal parts. When a suitable magnetic field is applied, the ferrite is magnetized, and due to the effect of anisotropy, an electromagnetic field as shown in Figure 3 (c) is excited on the ferrite junction. When a suitable magnetic field is applied, the ferrite is magnetized, and due to the effect of anisotropy, there is a signal output at branch "②", while the electric field at branch "③" is zero and there is no signal output. When also input from branch "②", branch "③" has output, while branch "①" has no output; When input from branch "③", branch "①" has output while branch "②" has no output. It can be seen that it forms a unidirectional circulation of "①" → "②" → "③" → "①", and the reverse direction is not connected, so it is called an RF circulator.
Product Display